근시, Near-sightedness(Myopia)
- 눈 가까이 있는 물체는 잘 볼 수 있지만 눈에서 멀리 떨어져 있는 물체를 잘 볼 수 없는 시력을 근시라고 한다.
- 근시가 있는 안구의 전후 직경이 비정상적으로 길다.
- 초점이 눈의 망막의 앞쪽 부위에 생기기 때문에 영상이 희미하게 생긴다(그림 참조).
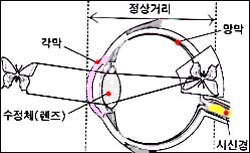
그림 32. 근시가 없는 정상 눈
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
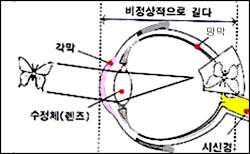
그림 33. 근시가 있는 눈
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
근시의 원인
- 근시의 확실한 원인은 모른다.
- 대부분의 근시는 유전성으로 생긴다.
- 안구의 전후 직경이 정상보다 더 길 때,
- 안구의 전후 직경이 정상보다 더 길지는 않지만 렌즈 자체의 굴절력이 정상보다 더 강할 때,
- 또는 렌즈가 비정상적으로 안구의 앞 쪽에 있을 때 근시가 생길 수 있다.
- 어떤 물체를 볼 때 눈 속으로 들어온 영상의 초점이 각막과 렌즈를 통과한 후 그 영상의 초점이 망막에 생기는 것이 정상이다.
- 그러나 근시가 있을 때는 영상의 초점이 망막에 생기는 대신 망막 앞 부위에서 렌즈 사이에 생긴다.
- 이런 이유로 근시를 가진 아이들은 눈 가까이 물체를 잘 볼 수 있지만,
- 눈에서 멀리 떨어져 있는 물체를 볼 때 물체가 희미하게 보인다. (그림 32, 33 참조)
근시의 증상 징후
- 근시의 증상 징후는 그 원인과 정도에 따라 다르다.
- 근시가 심할 때는 멀리 있는 물체가 희미하게 보인다.
- 근시가 있는 눈으로 어떤 물체를 볼 때 물체를 눈 앞 가까이 놓고 보든지,
- 아니면 가까이 가서 보는 경향이 있다.
- 수업 받는 중 될 수 있는 한 칠판 가까이에 앉으려고 하거나
- 무엇을 볼 때 눈살을 찌푸릴 수 있다.
- 이 때 근시가 있는 눈이 사시가 있는 눈처럼 보이기도 하고 사시도 생길 수 있다.
근시의 진단
- 증상 징후와 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 근시가 있다고 의심되면 소아청소년과에서 진찰을 받고 소아과의 소개를 받아 안과 전문의의 진찰 진단을 받는다.
근시의 치료
- 근시의 정도, 원인 등에 따라 치료한다.
- 일반적으로 어렸을 때부터 가진 대부분의 근시는 사춘기가 될 때까지 점차로 근시의 정도가 점차로 더 심해질 수 있다.
- 따라서 의사의 지시에 따라 정기적으로 눈과 시력 검사를 받고
- 적절한 오목 렌즈 안경으로 근시를 치료해야 한다.
Near-sightedness (Myopia)
• Myopia is a condition in which you can see objects close to your eye well but cannot see objects far away from your eyes.
• The anteroposterior diameter of the myopic eyeball is abnormally long.
• The image is blurred because the focus is on the front part of the retina of the eye (see figure).

Figure 32. Normal eye without myopia Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

Figure 33. Myopia Eyes Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
Causes of myopia
• The exact cause of myopia is unknown.
• Most myopia is hereditary.
• When the anteroposterior diameter of the eyeball is longer than normal,
• When the anteroposterior diameter of the eyeball is not longer than normal, but the refractive power of the lens itself is stronger than normal,
• Or nearsightedness can occur when the lens is abnormally positioned in front of the eye.
• When looking at an object, it is normal for the focus of the image that enters the eye to pass through the cornea and lens, and then focus on the retina.
• However, in myopia, the focus of the image occurs between the lenses in the front of the retina instead of on the retina.
• For this reason, children with myopia can see objects close to their eyes, but
• Objects appear dim when looking at objects that are far away from the eye. (See Figures 32 and 33) Symptoms of myopia
Symptoms, signs of myopia
The signs and symptoms vary depending on the cause and severity. • With severe nearsightedness, distant objects appear blurry.
• When looking at an object with a near-sighted eye, whether the object is placed close to the
• Or they tend to look closer.
• Try to sit as close to the blackboard as possible during class;
• You can frown when looking at something.
• At this time, the nearsighted eye may look like a strabismus eye and may develop a perspective view.
Diagnosis of myopia
• If you suspect that you have nearsightedness based on symptoms and examination findings, see the Pediatrics Department and receive a referral to the pediatrician for diagnosis and diagnosis by an ophthalmologist.
Myopia treatment
• Treat according to the degree and cause of myopia.
• In general, most myopia from childhood can be progressively more severe until puberty.
• So get regular eye and vision exams as directed by your doctor.
• Myopia should be treated with suitable concave lens glasses.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Gray’s Anatomy
-
제19권 소아청소년 안과 질환 참조문헌 및 출처
- Habilitation of The handicapped Child, The Pediatric Clinics of North America, Robert H Haslam, MD.,
-
Pediatric Ophthalmology, The Pediatric Clinics of North America, Leonard B. Nelson, M.D.
-
Pediatric Ophthalmology, The Pediatric Clinics of North America, Lois J. Martyn, M.D.
-
Pediatric Ophthalmology, Edited by Robison D. Harley, M.D.
-
The Pediatric Clinics of North America, David Tunkel, MD., Kenneth MD Grundfast, MD
-
Atlas Pediatric Physical Diagnosis Frank A Oski
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.